Rebuilding Mailchimp’s A/B Testing Experience
A unified A/B testing framework that simplifies creation, increases adoption, and fits seamlessly into real marketing workflows

Defined and delivered the vision for Mailchimp’s A/B testing platform—securing a dedicated initiative and driving a 140% increase in exploration, 23% repeat usage growth, and a clearer path for marketers to test with confidence.
CONTRIBUTIONS
Research qualitatively & quantitatively to understand the problem space
Present vision & impact to leadership, leading to formation of a dedicated team for this initiative
Create & communicate references such as design system & principles for consistency
Led design in collaboration with designers, engineers, and product managers on multiple teams utilizing A/B testing
Role
Lead product designer
Team
1 product manager
4 engineers
Timeline
2024 - 2025
Problem
What is A/B testing
A/B testing is an experimentation method that helps marketers compare variations of a campaign to understand what resonates with their audience and make data-driven decisions.
Opportunity gap
Although A/B testing is critical for marketers, Mailchimp saw a low established usage rate of 0.34% of its tool among eligible users, indicating issues with the product experience.
95% of users had not used A/B testing in Mailchimp
USER NEED
Marketers need to A/B test as an essential method to:
Understand their audience
Improve strategy & tactics
Increase performance & key metrics
59% of companies are A/B testing marketing channels
"If we’re not testing, we’re not marketing"
User PROBLEM
Mailchimp users are rarely testing due to:
Poor discoverability
Limited functionality
Low interpretability & actionability
Less than 1% of Mailchimp users are A/B testing
"I would get frustrated at this point and stop A/B testing"
Why it matters
As businesses grow, so must their marketing capabilities.
If marketers can't perform essential actions such as testing, they lose confidence in the platform and churn toward more capable tools.
"The biggest difference between Mailchimp and (competitor), and one of the main reasons we switched, was the ability to A/B test automations”
Key metrics
Success for an experience which improves user discoverability, usability, and interpretability can be measured by the following metrics:
Usage rate
Completion rate
Repeat usage rate
Mailchimp's current A/B testing experience doesn't meet users' needs
Solution
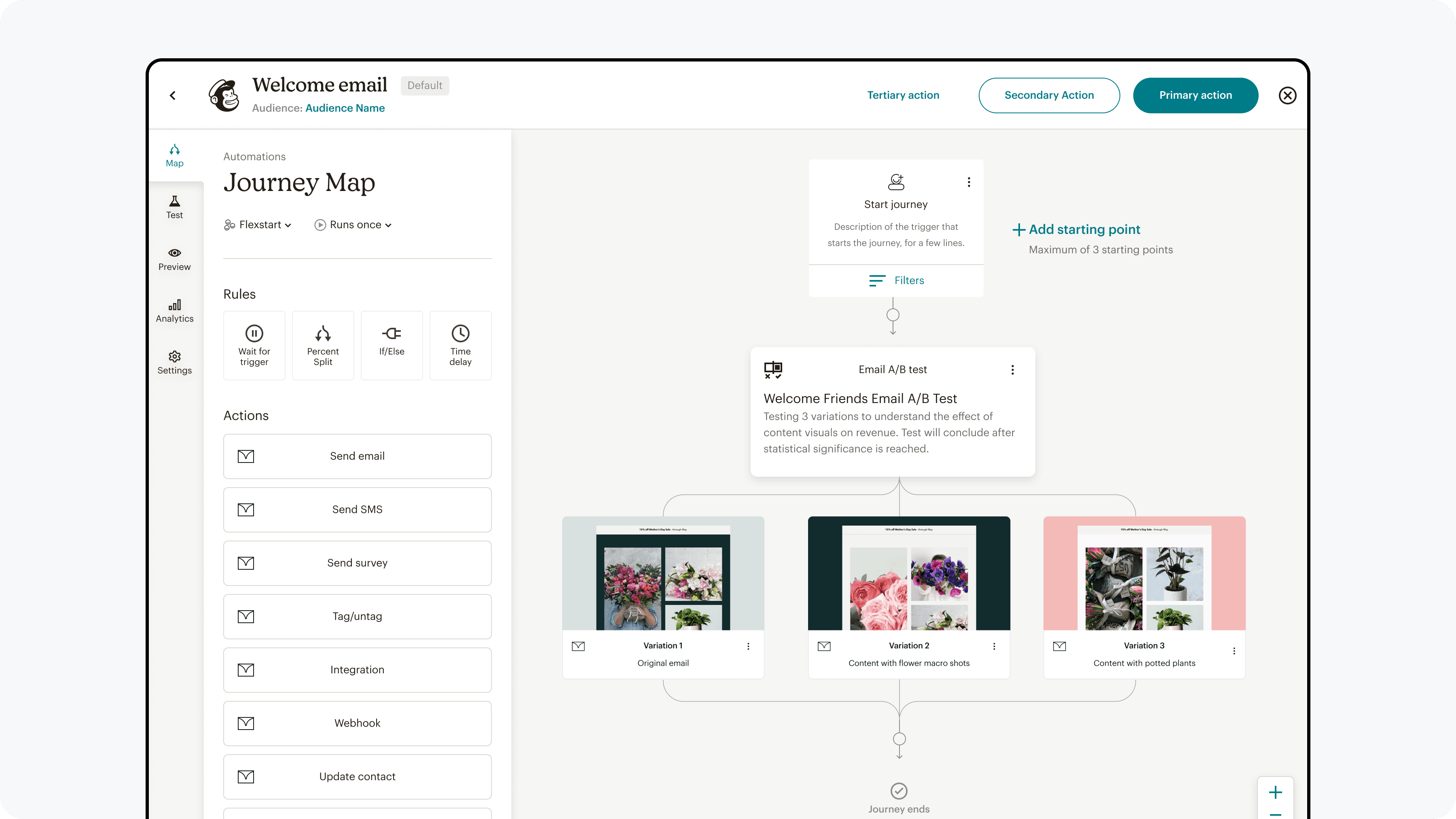
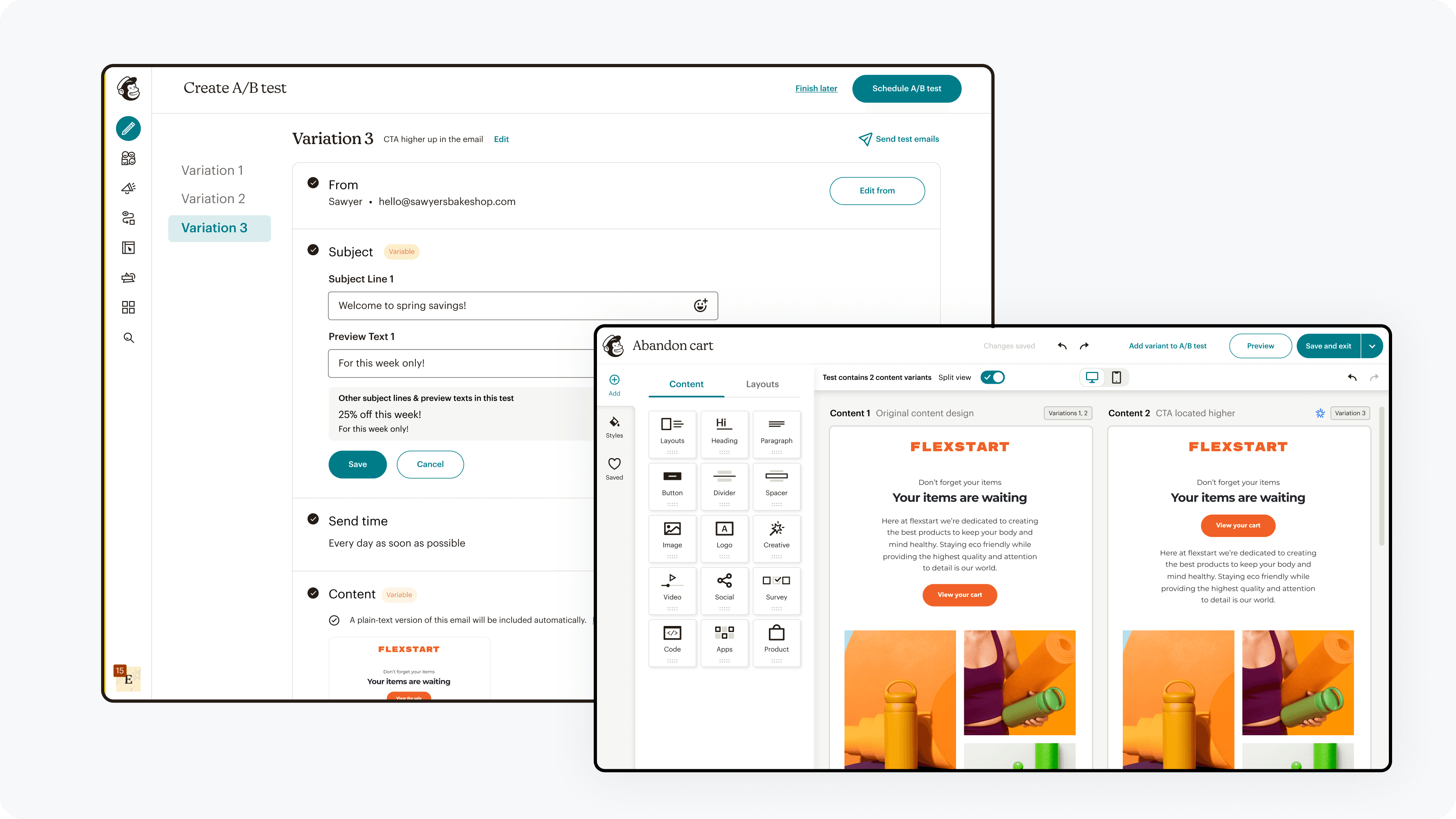
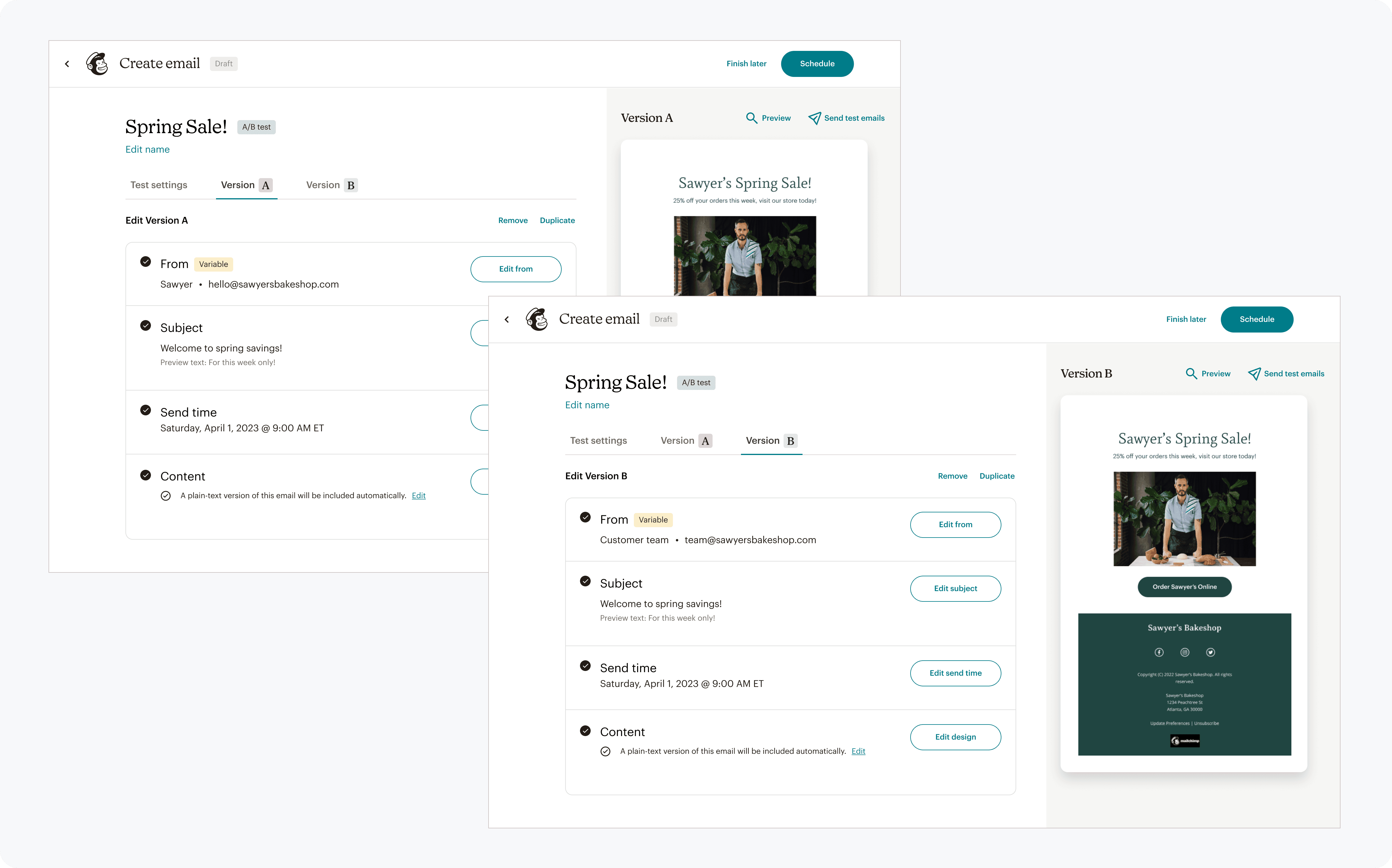
Final experience
A unified A/B testing experience that works across channels, supports simple to advanced tests, and provides clearer guidance and insights at every step.
Discoverability
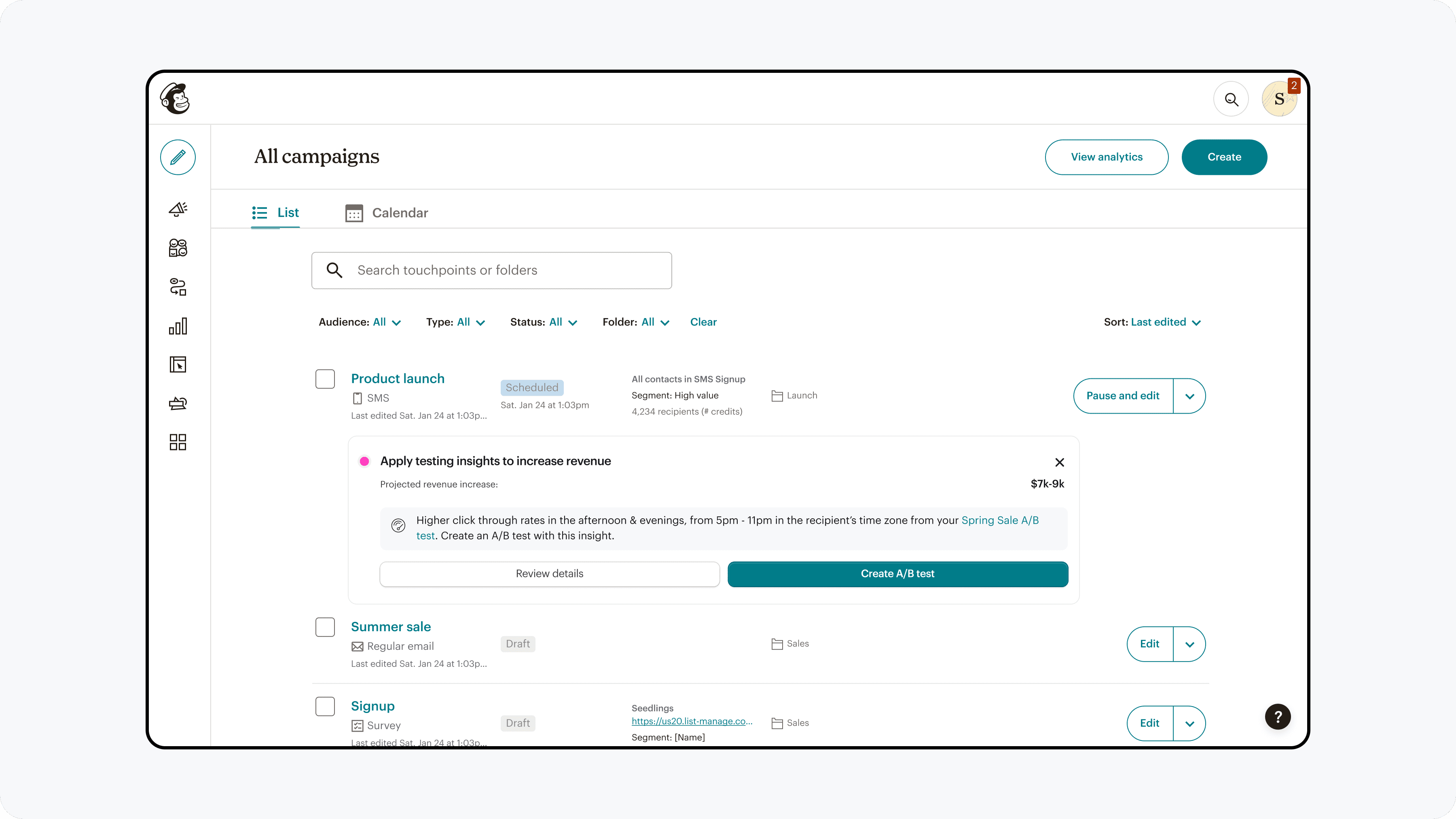
A/B testing entry points were aligned with marketers' natural workflow of creating a base campaign and then adding a variable to test.
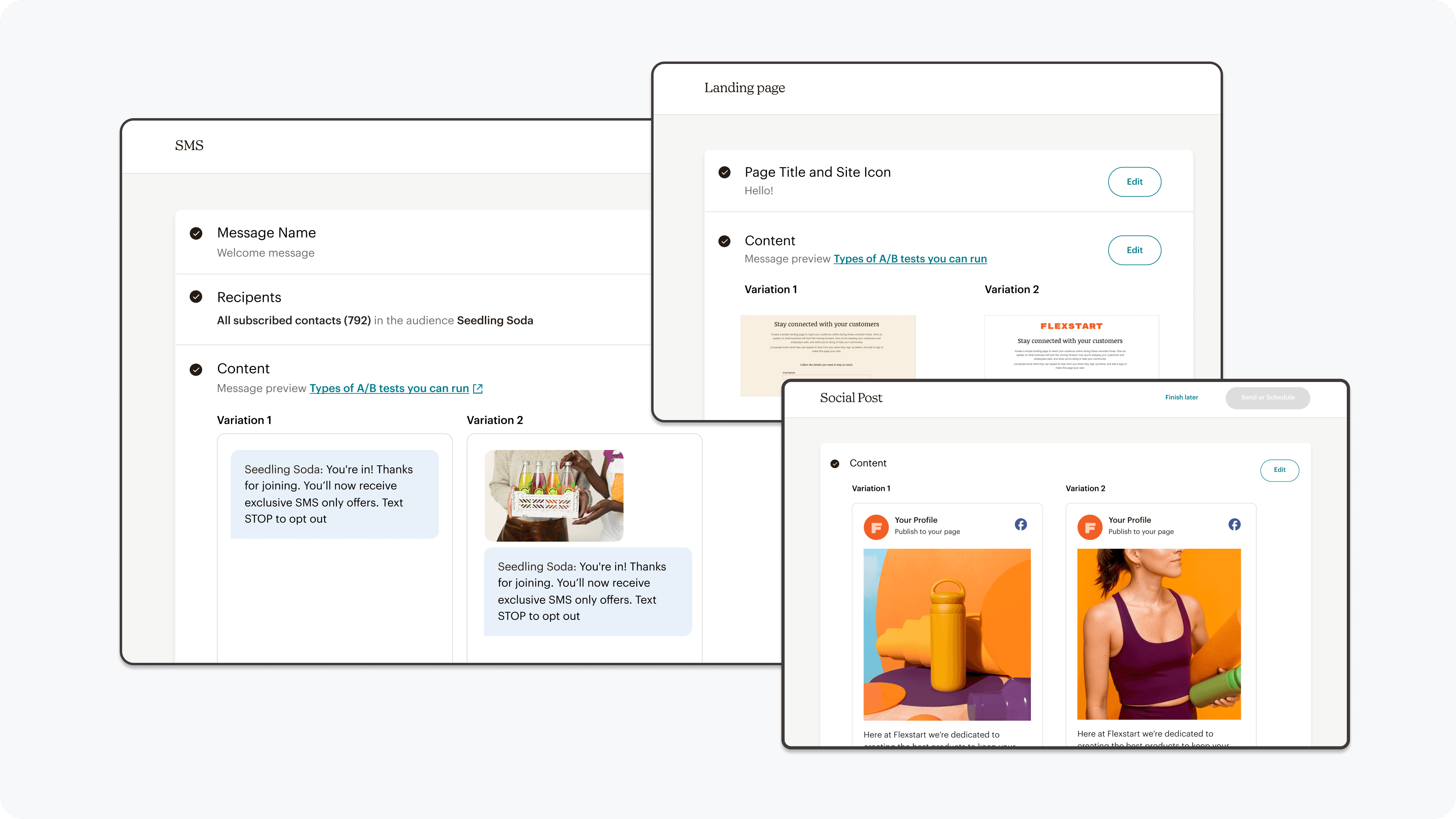
Functionality
A/B testing capabilities were expanded & refined to enable and guide users to create effective tests
Interpretability
Results were presented in a way which allowed for easy analysis, gathering insight, and direction for subsequent actions.
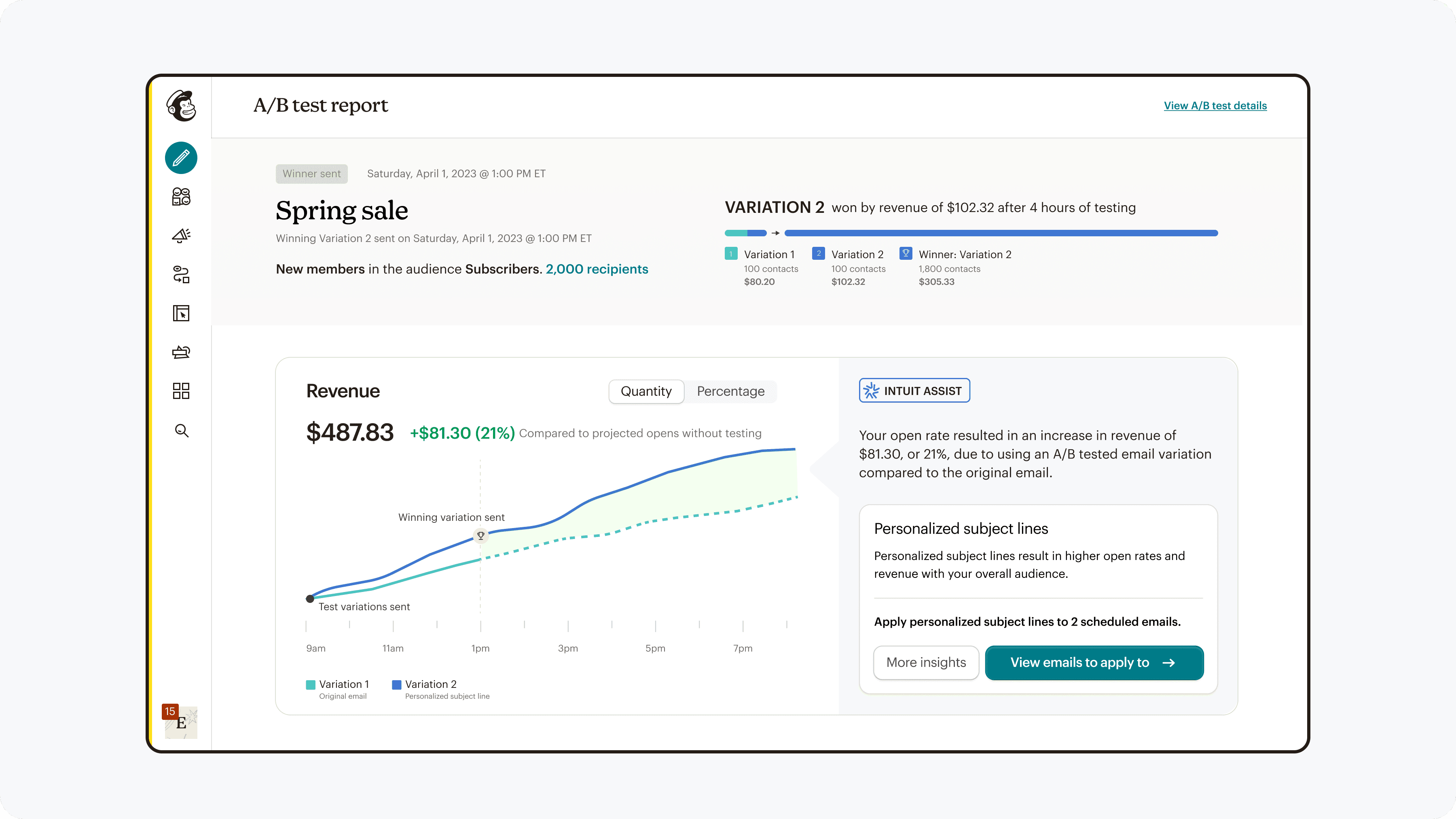
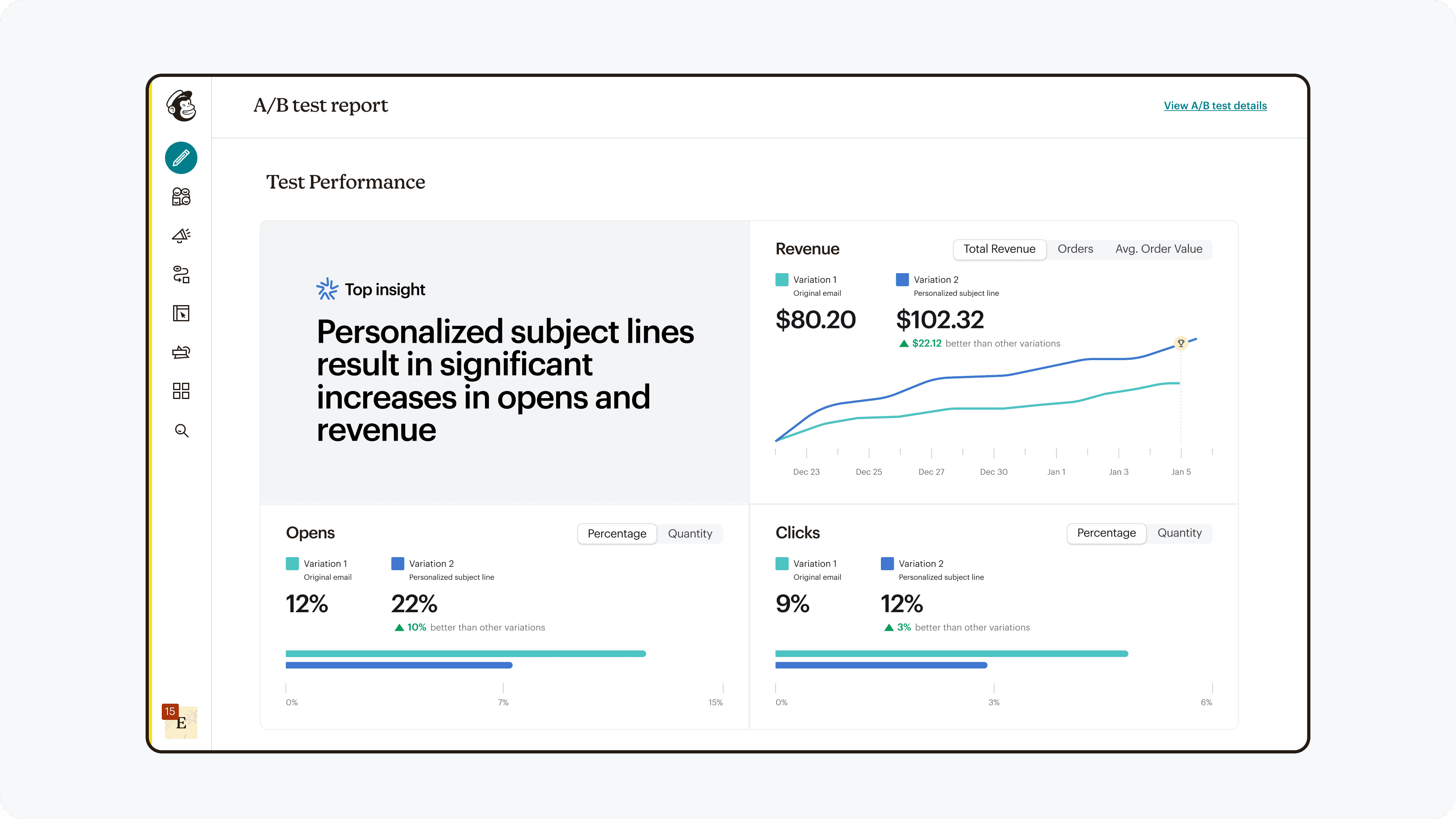
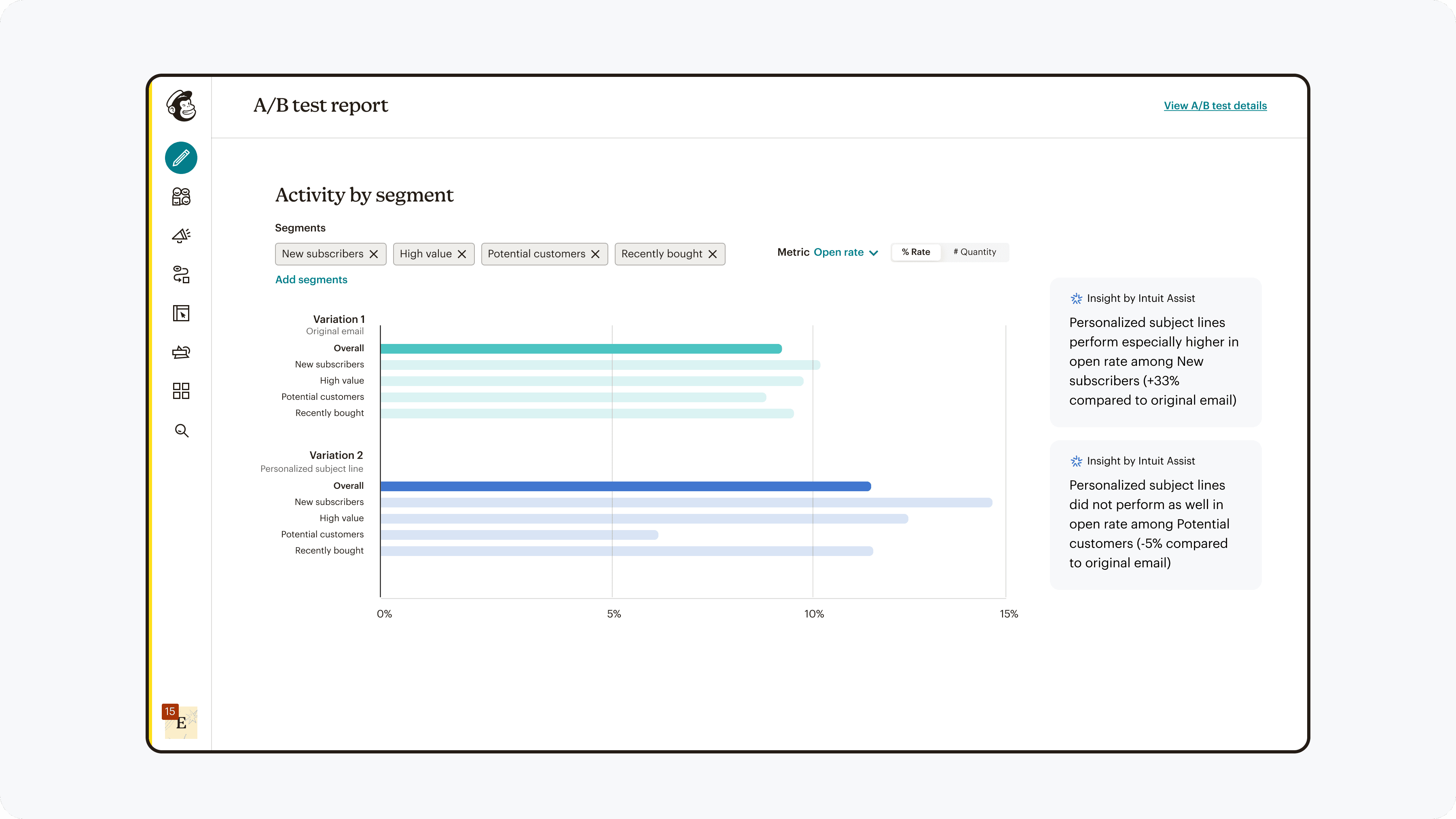
Results
The team was able to launch A/B testing for SMS, and afterwards for forms. After a month of collecting data for SMS, we found the following results:
Discoverability:
Increase of 140% exploration rate
Functionality:
12% increase in completion rate
Interpretability:
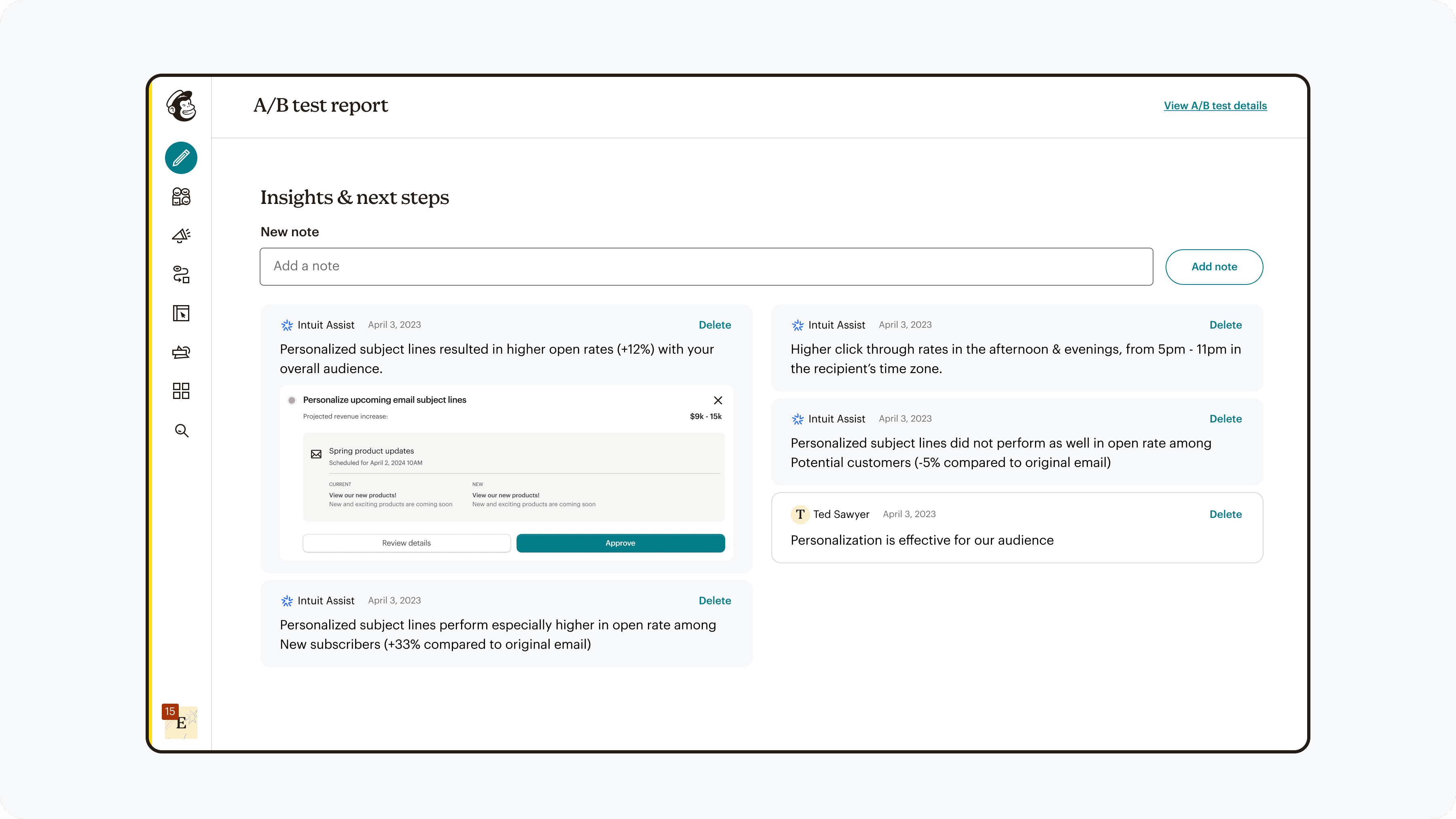
220% increase in repeat usage
This shows that the changes were effective, and with monitored results for forms as well as deeper quantitative & qualitative research, can make any needed adjustments and continue to roll out to other marketing channels.
Research
Goals
Took lead in conducting effective research from start to finish of this project, with the following goals:
Manage & prioritize research methods throughout the process
Understand user behaviors & attitudes
Generate insights that drive data informed decision making
Communicate & collaborate with cross-functional stakeholders
Methods
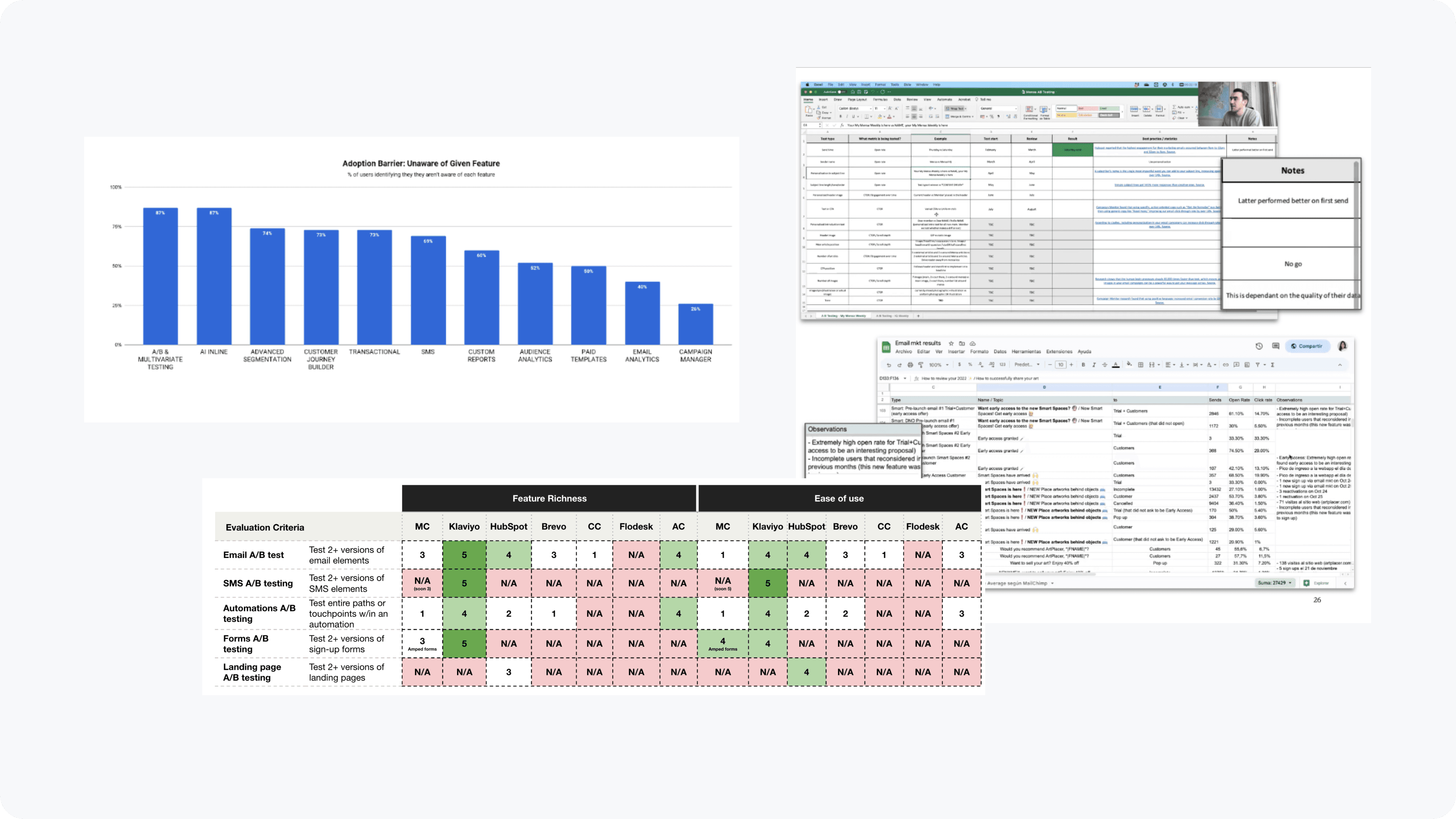
Each stage of the process required different methodologies.
I utilized current research & data to inform research plans for subsequent exploratory research. After each round of designs & releases, additional research & monitoring were needed to ensure we were heading in the right direction.
Current landscape
Synthesize 2 past research studies
Data analysis using Looker, Amplitude, & custom data
Competitive research with the 5 relevant competitors
Heuristic evaluation of the current experience
Research papers of best practices
New insights
Primary, in-depth interviews with 20 target users
Diary study & analysis of artifacts
Concept testing with 10 users
Interviews with 2 subject matter experts
Card sorting
Surveys
continual refinement
Usability testing, both moderated and unmoderated
Consultations with internal subject matter expert
Data monitoring of usage & key actions
Data on current product usage, competitive research, and qualitative research with user artifacts
Insights & outcomes
Research was used to create & inform the following:
Presentation to leadership which justified formation of a dedicated team
Strategic direction based on user perspectives & behaviors
Clear mental model to align product information architecture
Guidelines on how AI can best assist marketers with testing
Strategy
Project priorities & goals
When considering designs & inter team negotiations, it was essential to outline each teams' priorities.
Design
Meet user needs & minimize friction
Scalability & consistency
User guidance, including utilizing AI capabilities
Engineering
Technology stack that is capable of future features
Minimize duplicate codebases
Reusablility
Business & product
Contribute to key company metrics
Speed to delivery
Reduce risk
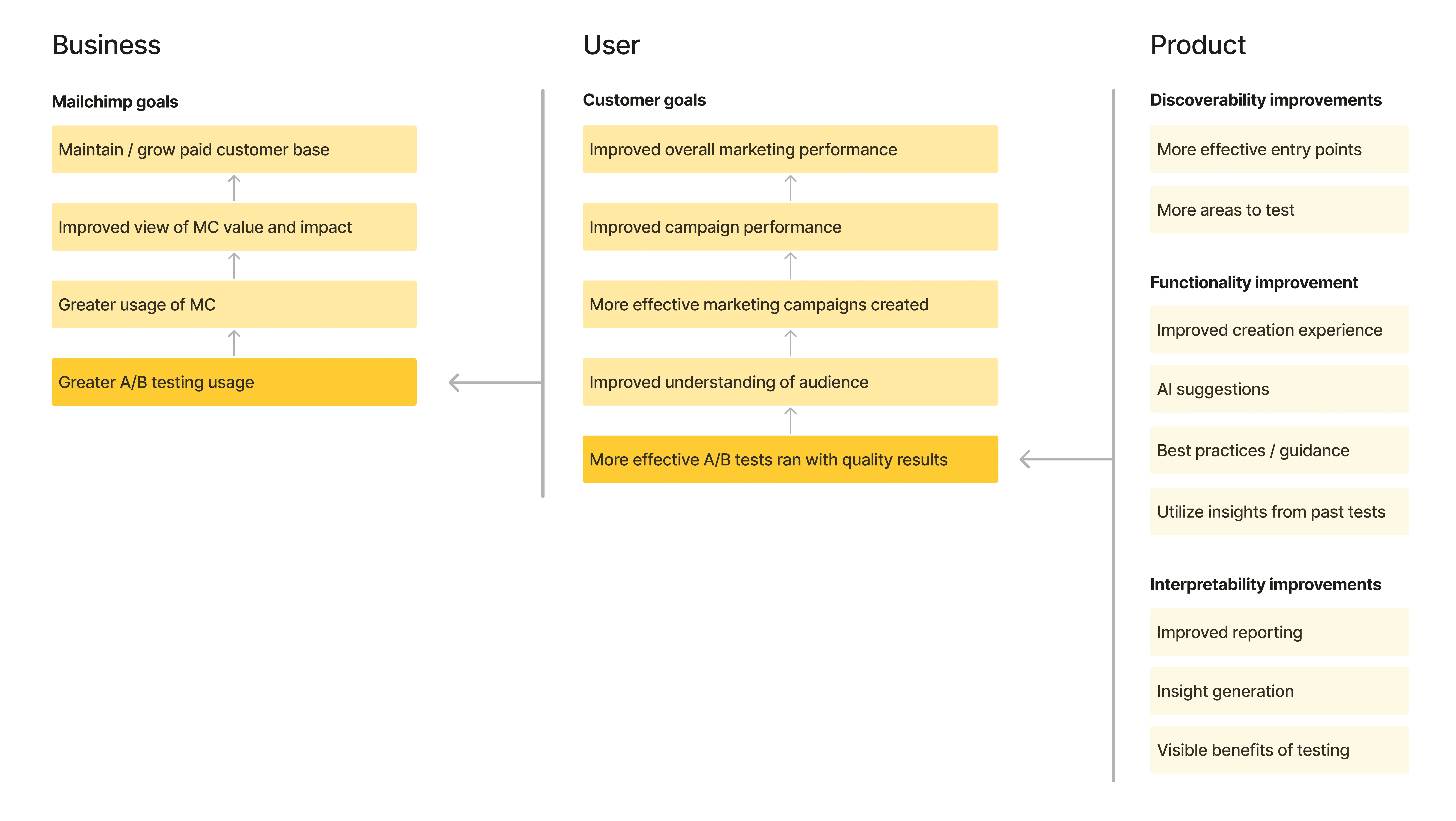
When also considering end goals for this initiative, it was essential to align how elements of the experience would ladder up to high level impact that business cared about.
Lining up product improvements with user & business needs
Key questions
I worked with product and tech leads to answer the following questions. I did so by anchoring direction to the research, understanding the priorities of each partner, and finding compromise where needed.
Where to introduce testing first?
To balance risk while maximizing learning, we launched A/B testing in SMS first—a smaller, highly motivated user group—before expanding to email, Mailchimp’s highest-visibility and highest-impact channel.
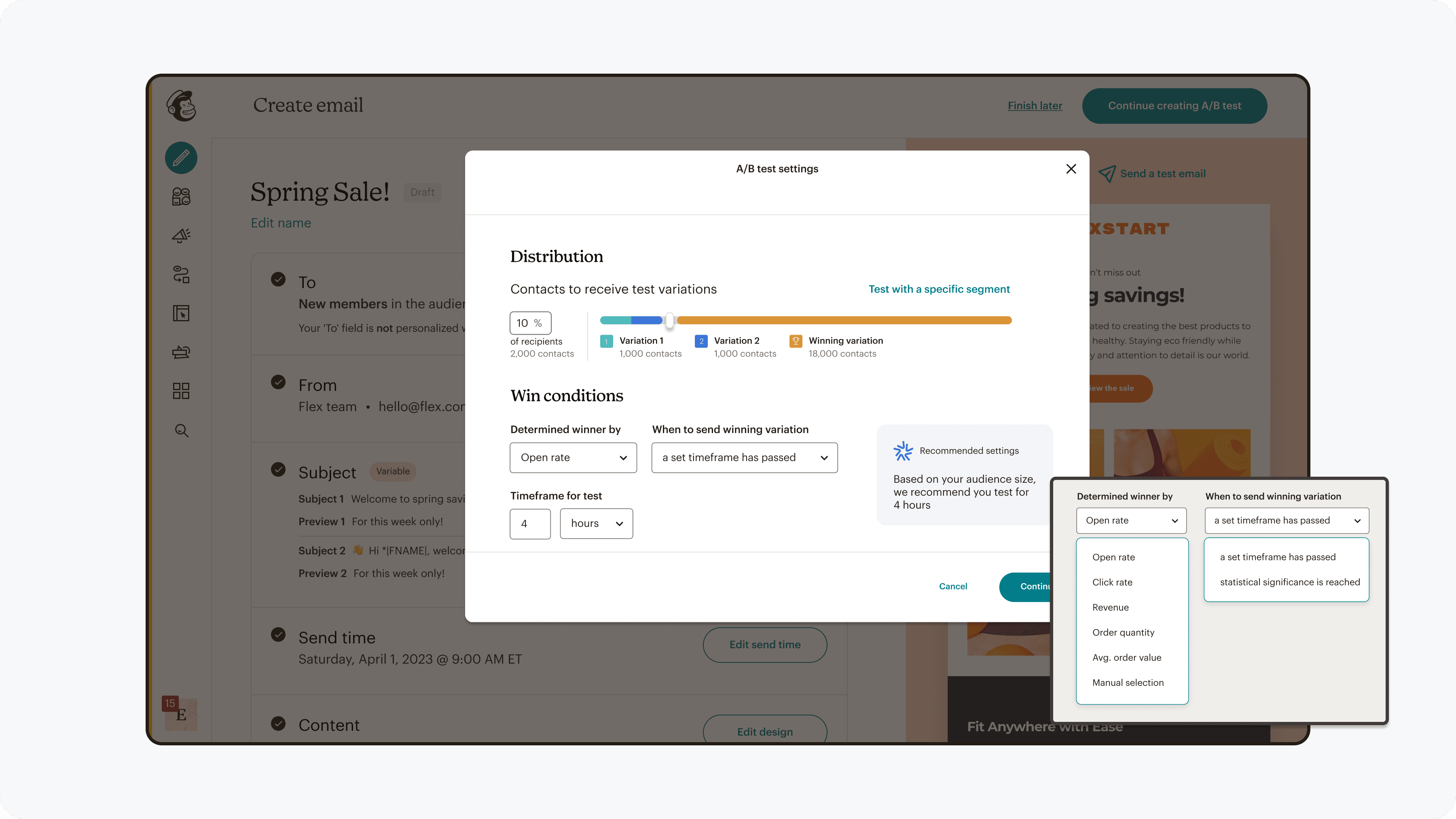
What scope of testing is allowed?
We defined the right balance between flexibility and guardrails by evaluating test scopes—from individual fields to cross-channel assets. Based on user mental models and best practices, we enabled testing entire assets, ensuring meaningful insights without over-complicating setup.
How can AI be leveraged to help?
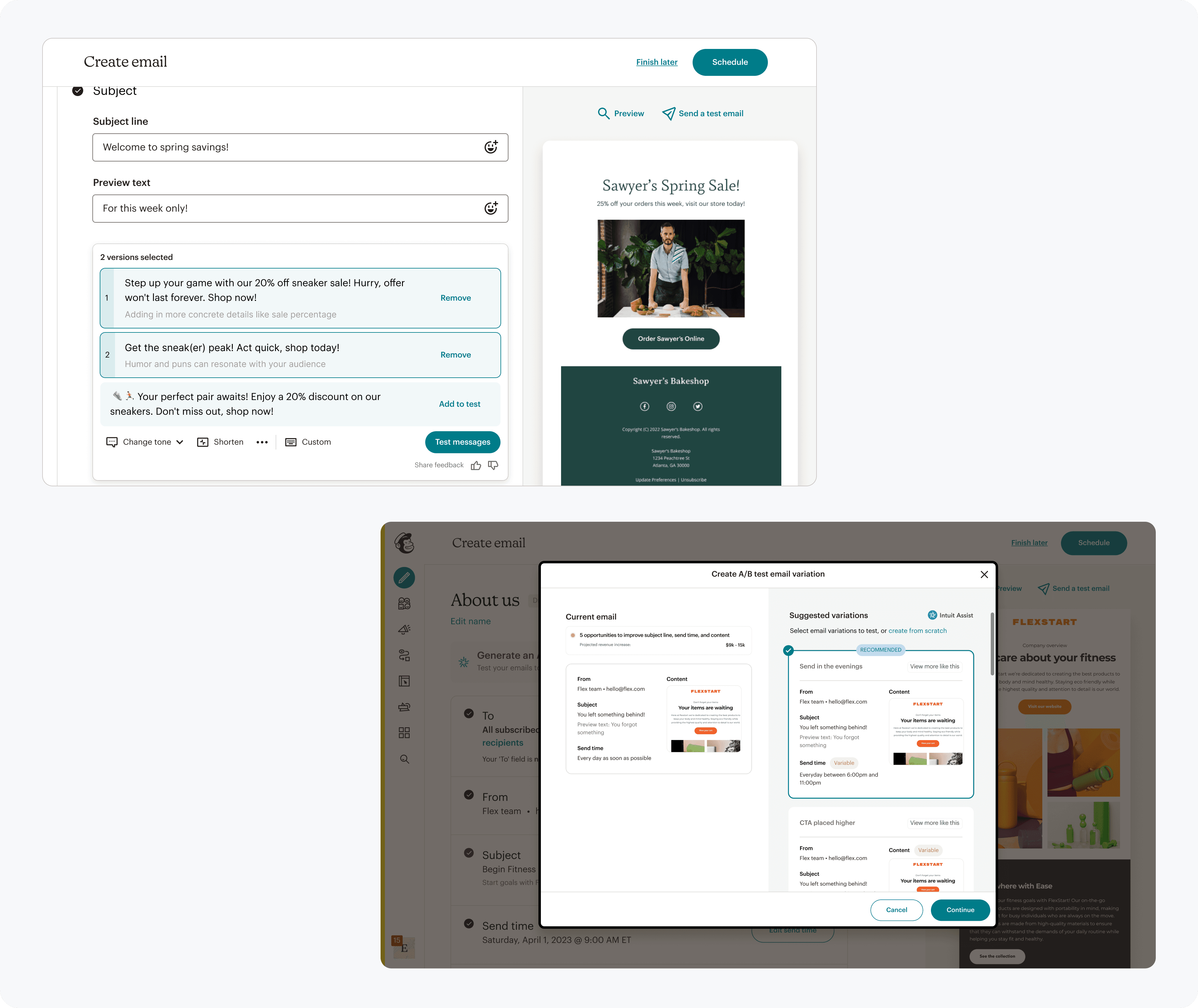
To meet rising AI expectations without creating low-quality output, we focused AI on high-value moments: generating test inspiration and helping interpret results. Research showed these areas delivered clarity and confidence without replacing user intent.
Design process
Team alignment
Alignment among stakeholders was needed to ensure cohesive communication.
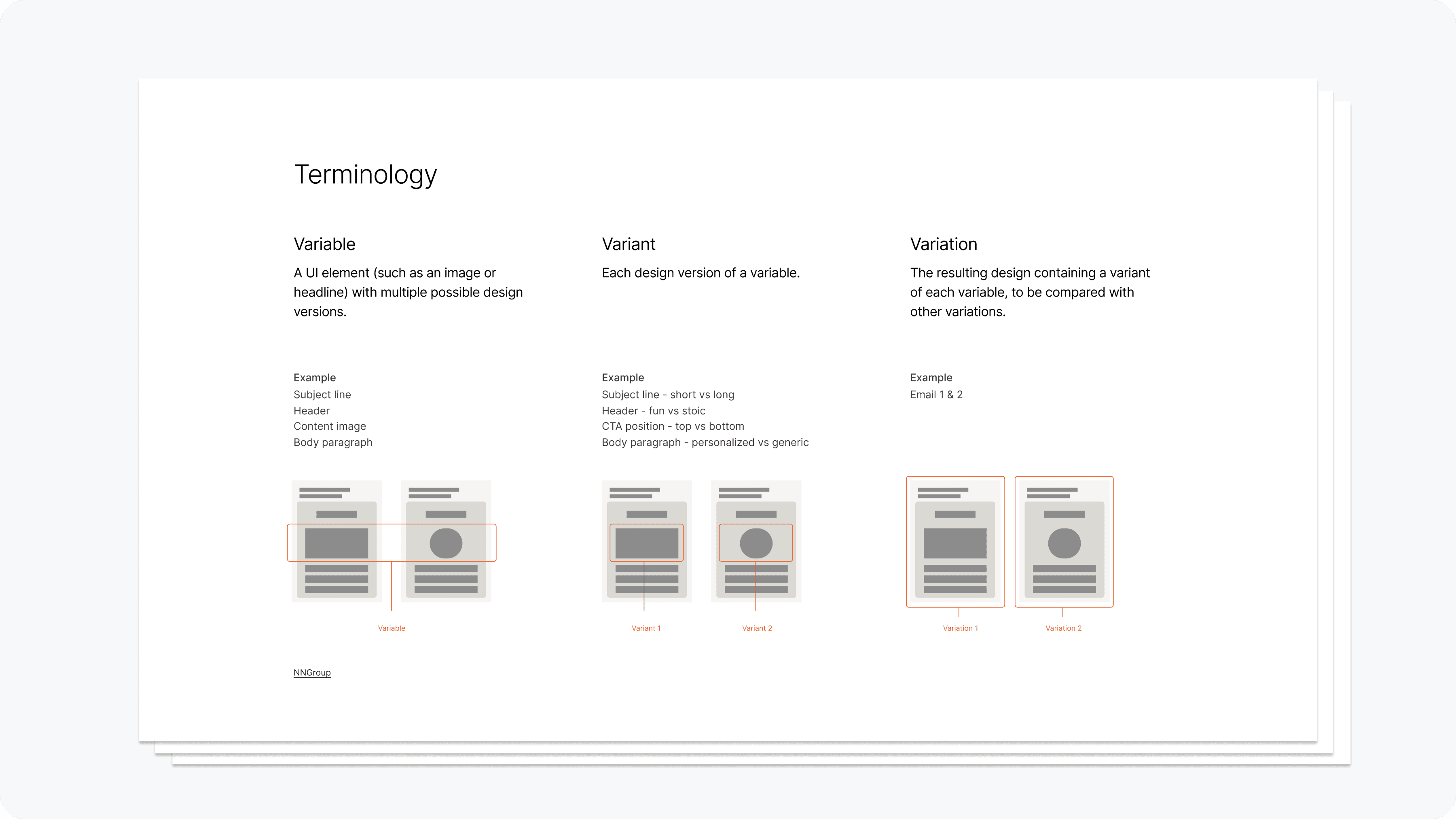
Some areas of alignment included a glossary based on technical documentation & intuitive common terminology which was helpful both internally and in guiding product content language.
Reference material for internal alignment
Design principles
The following were principles used to guide feature prioritization and design decisions
Flexibility:
Adapt to unique & evolving user needs
Guidance:
Provide starting points & education moments in context
Consistency:
Utilize patterns that apply to all areas of testing
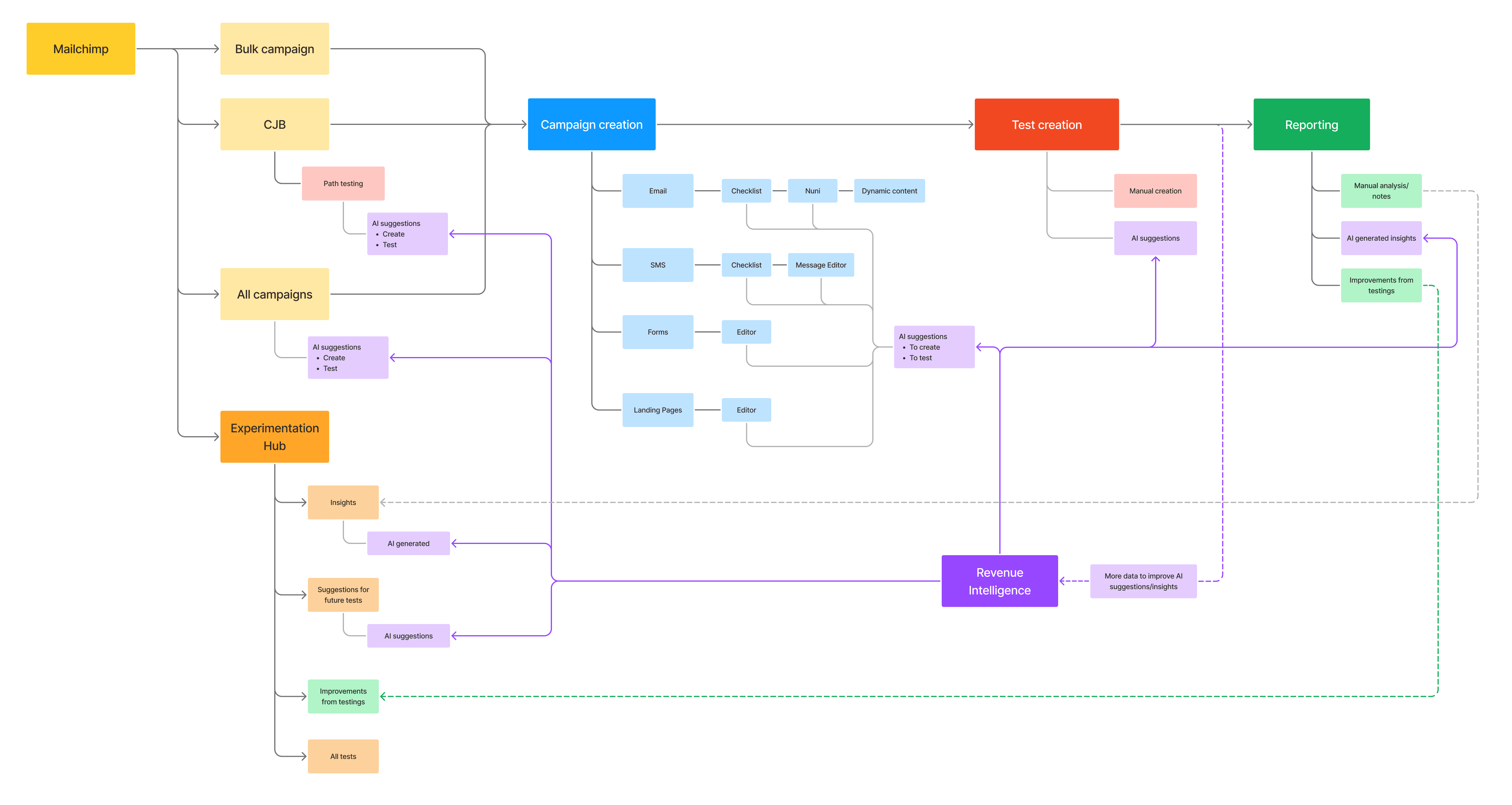
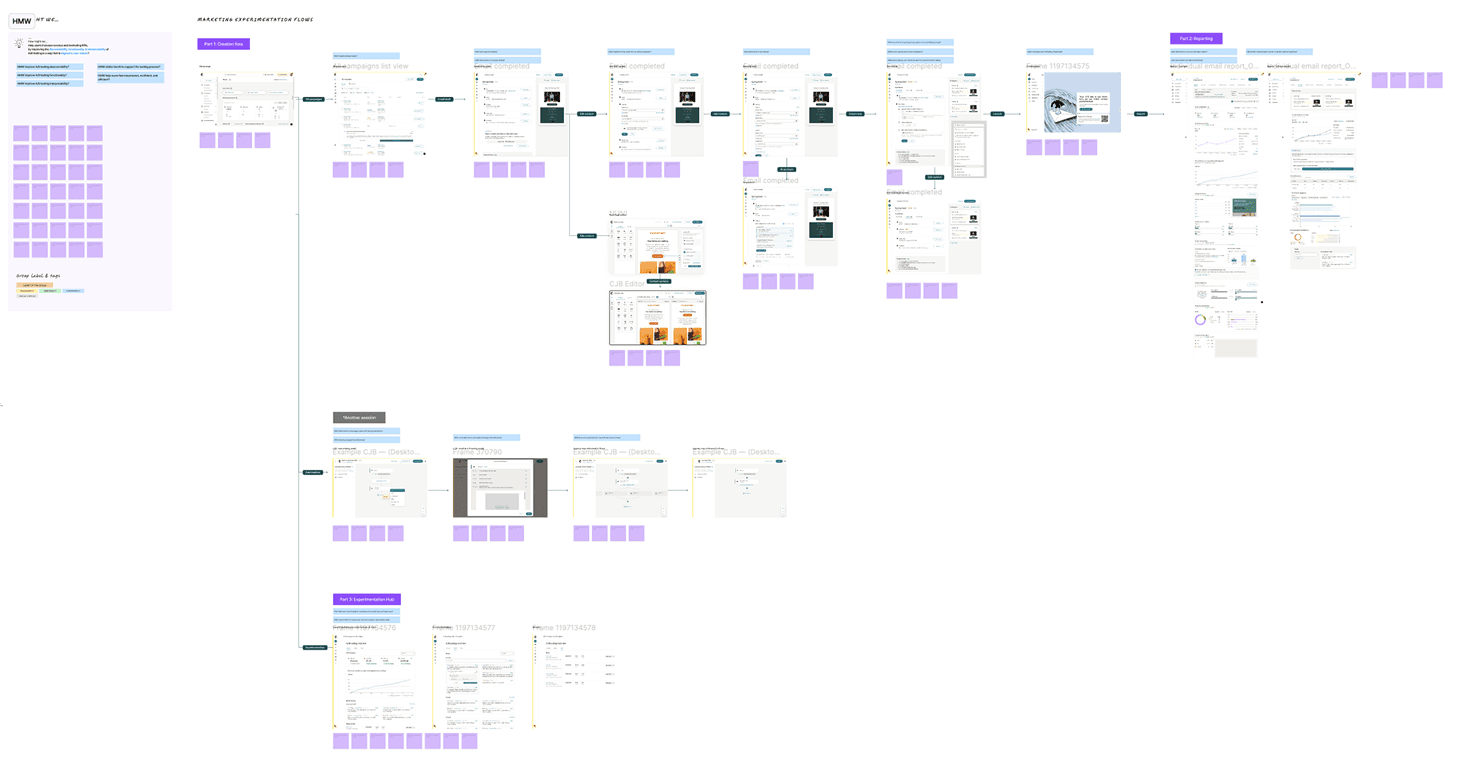
User flow & touch points
Creating a map of the overall user flow & touch points for A/B testing helped orient and contextualize the end to end experience throughout the design process.
High level user flow through the product
Ideation
In a team session, I lead a workshop to ideate in context to the varying stages of the user journey.
Tied to each were insights related to user needs & problems to help direct the ideas.
Ideation workshop with context of the product workflow
Explorations were made for various flows, layouts, and features.
Low fidelity mockups were quickly created for breadth of ideation.
Low fidelity explorations of diverging concepts
Prototyping & testing
Features that were critical were prioritized to be tested, as well as experiences that answered any unknown questions about user expectations.
Testing prototypes across common scenarios
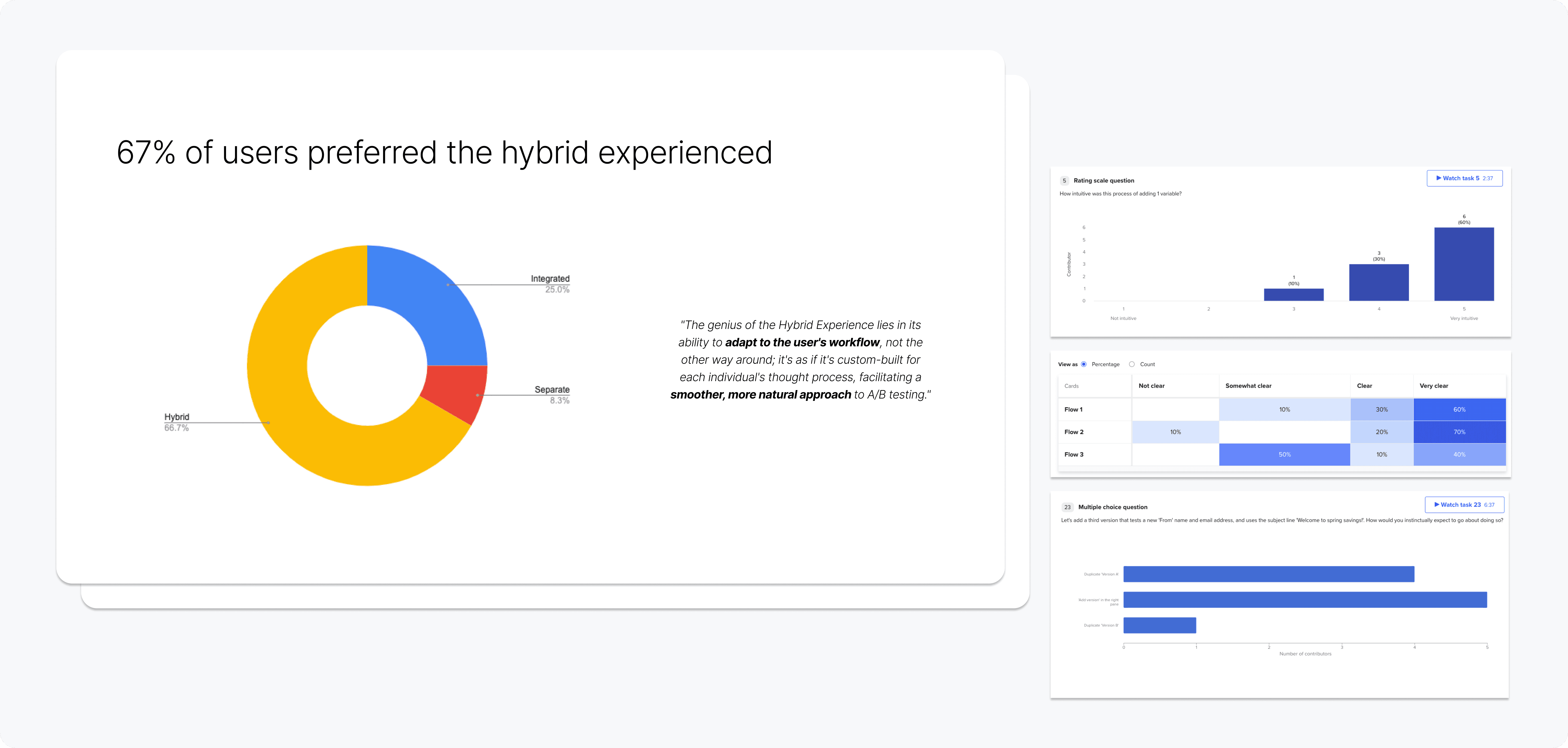
There was an initial moderated test with 10 users to be able to ask questions and understand nuanced behaviors.
Afterwards, multiple unmoderated tests were conducted for quick validation. The results were synthesized and presented to the team to establish clear direction.
Analysis from concept & usability testing
Design decisions
Several key design decisions were made, utilizing design principles, collaboration with cross functional teams, and evidence from qualitative & quantitative research. Below are some major decisions that were deduced through testing.
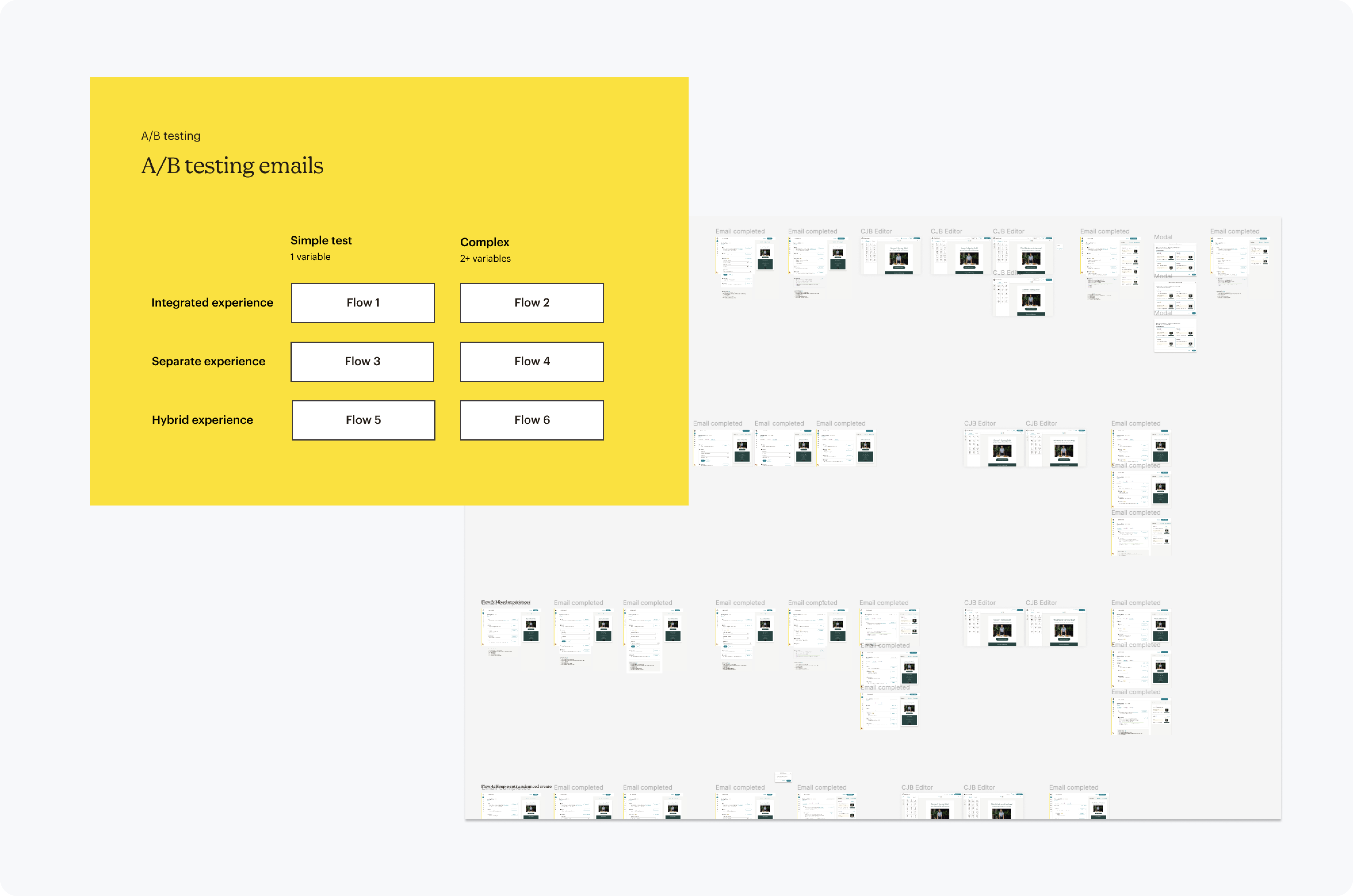
Hybrid workflow
A workflow that is familiar when creating field variants while building the base campaign, and then clearly an A/B test when refining and reviewing test details.
The tension was whether or not to fully integrate the experience in the base experience, to fully have a separate experience, or a hybrid.
Through synthesis of user behaviors during testing, users need a familiar environment when creating base campaigns & field variants, however, a separate testing environment allows for intuitive test set up and review.
Shifting experiences from base email editing, to A/B testing
independent campaign assets
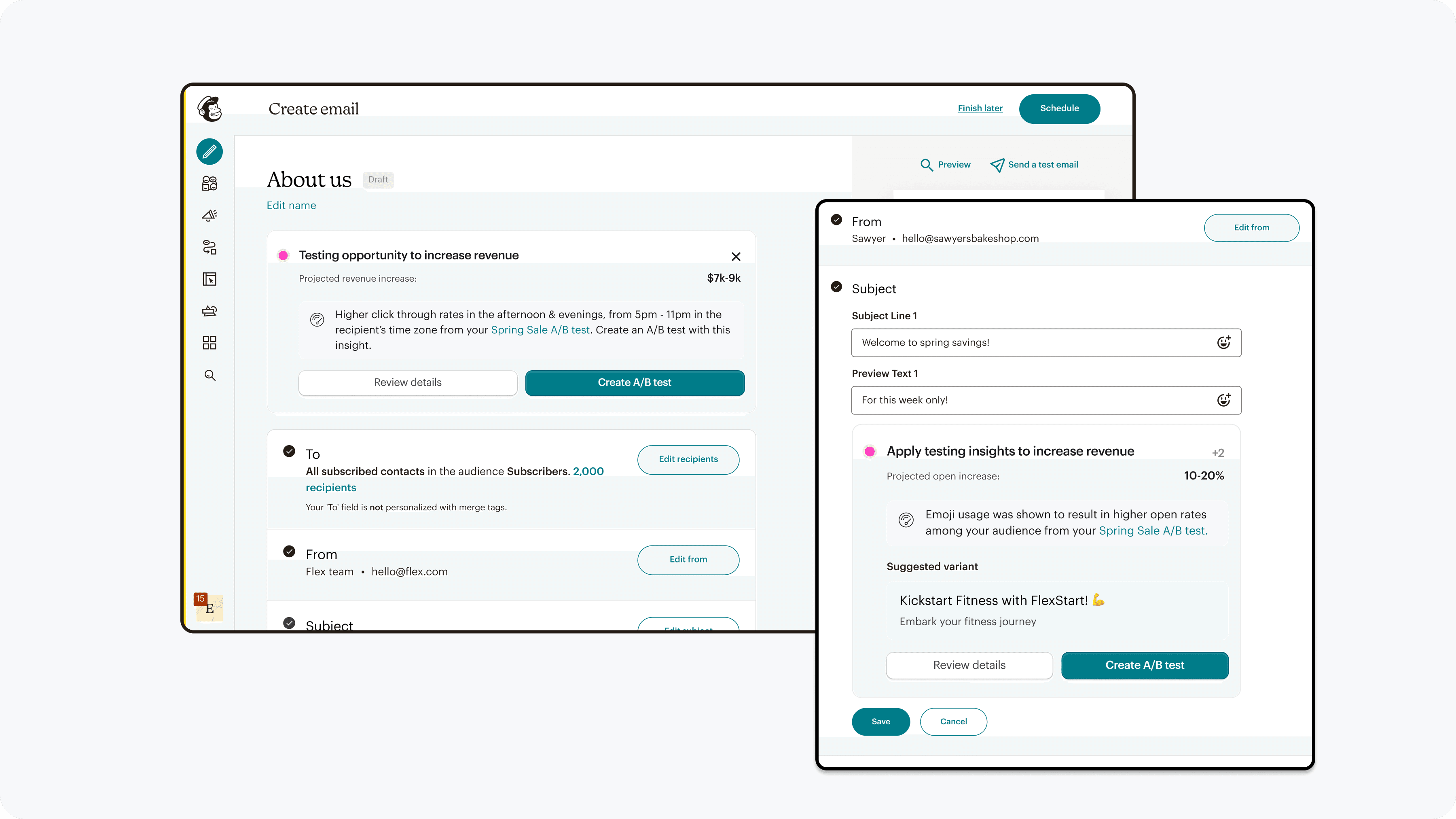
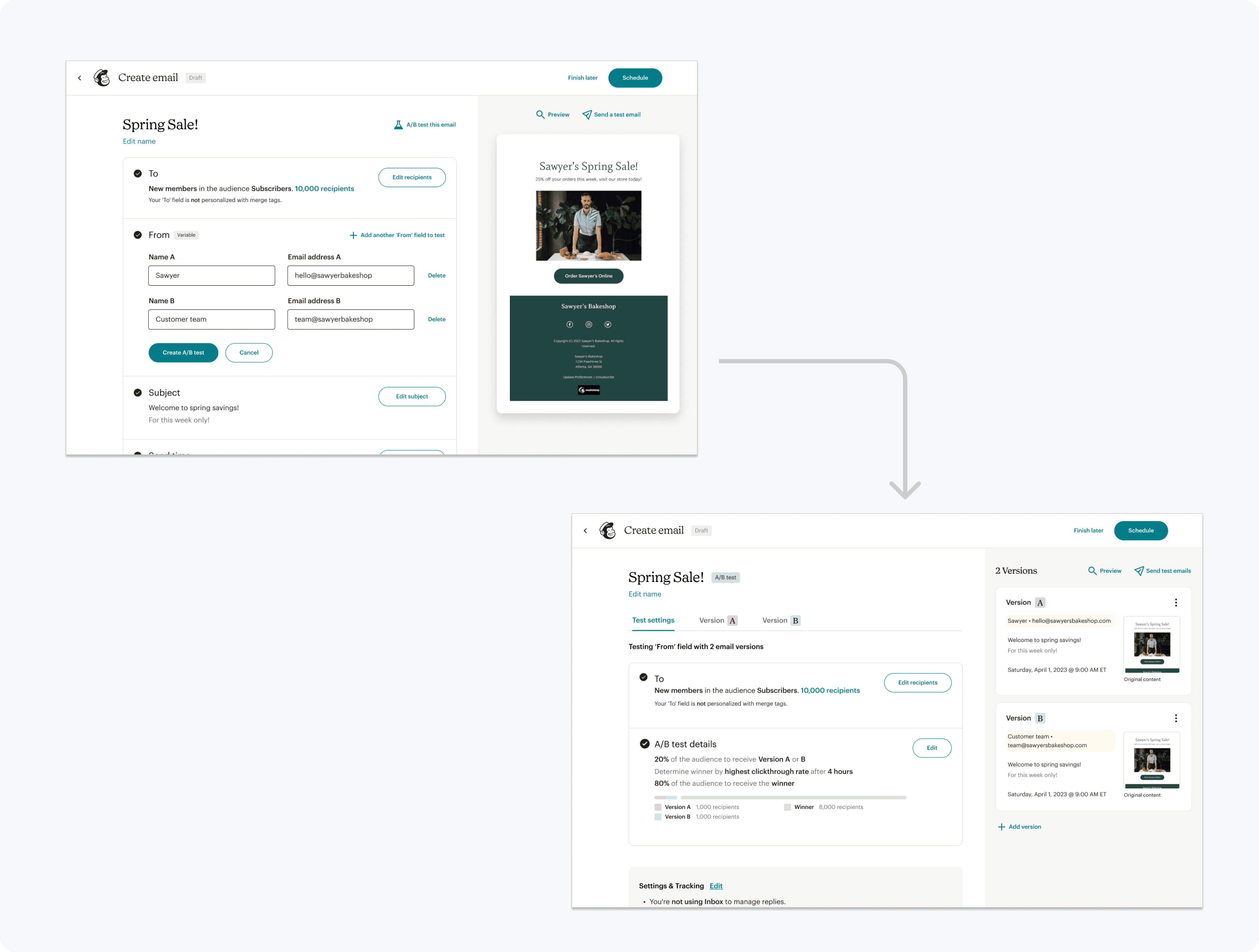
Independently editable campaign variations will be created to empower users to be the expert in how they craft their tests.
Though in best practices tests should only have one variable & change at a time, sometimes what is tested such as subject matter is more nuanced and require changing multiple fields like subject line & content to adequately test.
This led us to prioritize the ability for users to independently edit each campaign, which also aligns with what users expect when creating a test.
Each campaign version can be edited independently
With AI assistance, provide choice at varying levels
Users expected AI to help generate alternatives to test, but they needed to still feel in control.
Through choice and reasoning for generated choices, users gained confidence and a sense of autonomy in creating a test they wanted.
AI suggestions at varying levels of the creation process, with explanations for each option
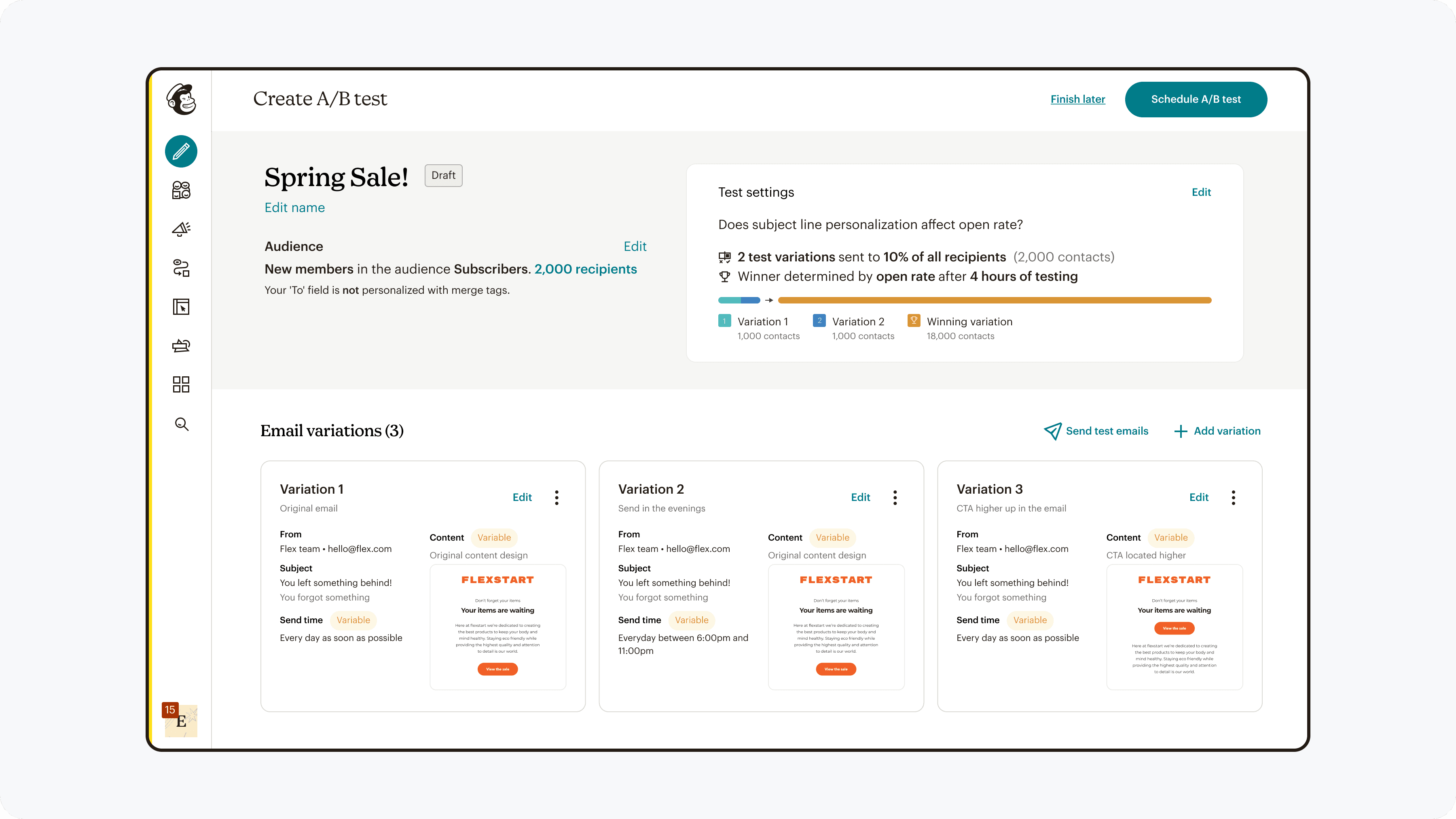
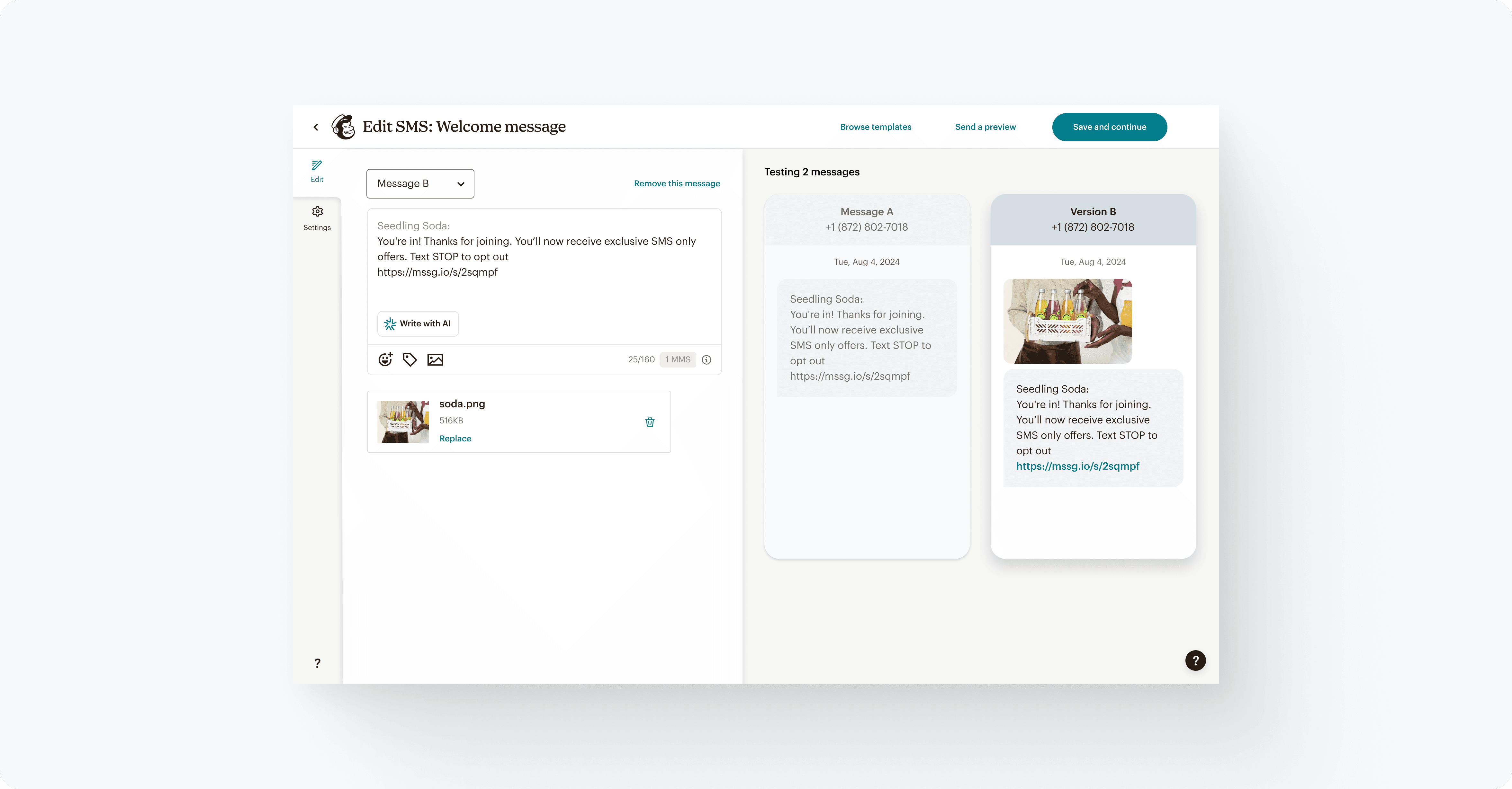
Comparison
Reviewing variations side by side is essential to establish confidence before testing.
We noticed users flipping back and forth between campaign versions to check the variables & constants before sending out their test. In order to better facilitate this need for visual verification, side by side comparison was added.
Providing a way to quickly compare versions
Key deliverables
Design system
Established components & patterns for A/B testing, which were integrated into the larger product design system.
Roadmap & designs
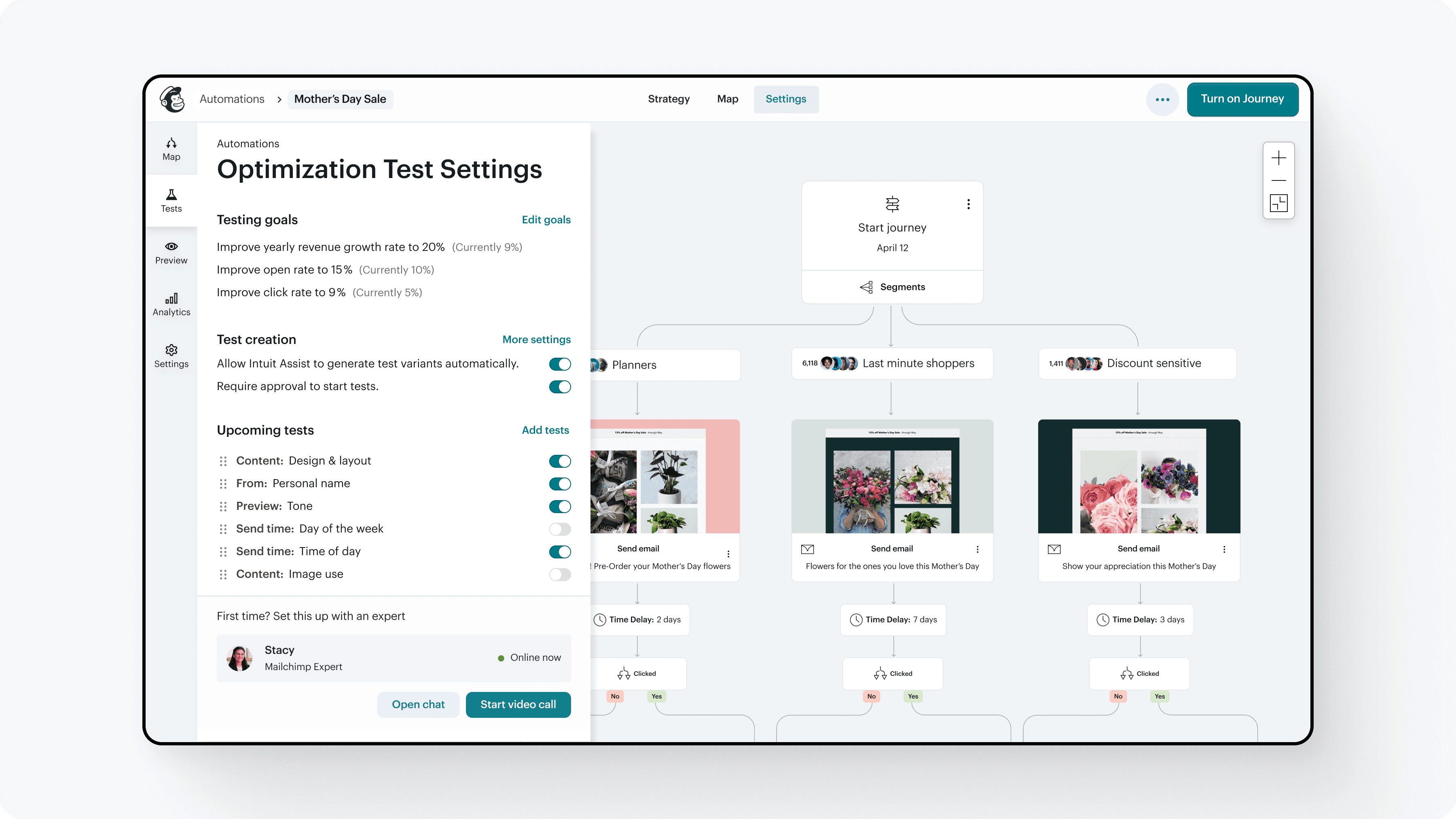
Roadmap & designs for A/B testing across all campaign types, across walk, crawl, run capabilities.
Sunset plan
Sunset plan & experience to archive the old experience and transition users to the new one.
SMS A/B testing launch
Launched A/B testing for SMS which showed improvements in performance across all metrics.
Reflections
Initial launch takeaways
The new A/B testing experience has proven effective across SMS and forms, establishing a strong foundation for expansion into additional surface areas.
While broader rollout phases were defined, leadership changes and shifting priorities introduced timeline variability.
Despite this, the future state of A/B testing at Mailchimp remains clearly defined—with a shared vision, reference guidelines, and validated user value ready to scale when priorities realign.
What I learned
Single source of truth
When a feature spans multiple surfaces, a single, shared source of truth is critical to keep product, design, and engineering aligned, which reduces downstream rework, as well as maintains a consistent user experience.
Juggling priorities
Teams operate against different success metrics; understanding those incentives early allows you to frame the product in terms of shared outcomes, accelerating alignment and decision-making.